How Ultrasonics Work.
Ultrasonic can be used to measure the distance between a sensor and an object by sending ultrasonic waves. Once the waves hit the object, they are reflected back towards the sensor, and the distance can be calculated by using well-know speed of sound.
It is important to remember that the speed varies with temperature. This post assumes 22 degree Celsius, where the speed is 344 m/s.
More basics can be found in Texas Instruments - Ultrasonic Sensing Basics
HC-SR04 internals
As specified in the documentation, the module is capable of measuring distances between 2cm to 4m. To initialize it, set the Trigger and Echo to low. Once ready, set the Trigger to high for 10us to send an acoustic burst and measure how long it takes to receive it back in Echo.
Don’t forget that the acoustic signal must always travel twice: from the module to a target and then back. Therefore, the total time must be divided by 2.
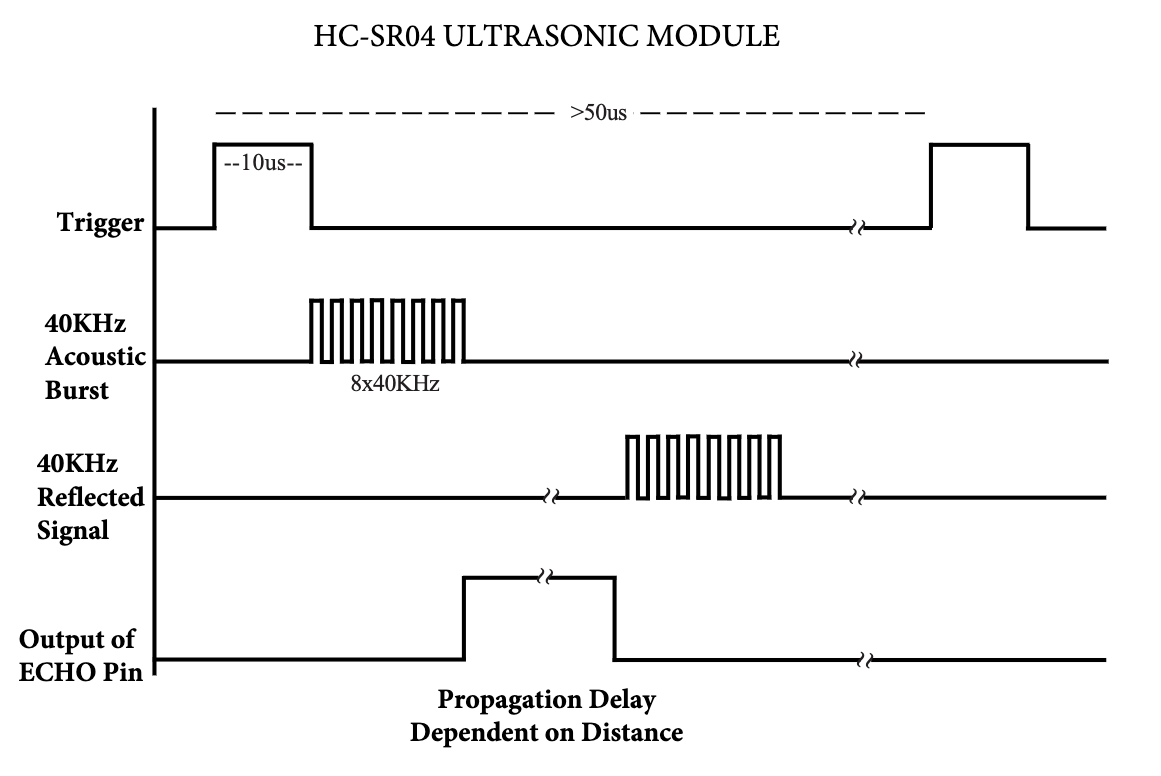
Download HC-SR04 documentation
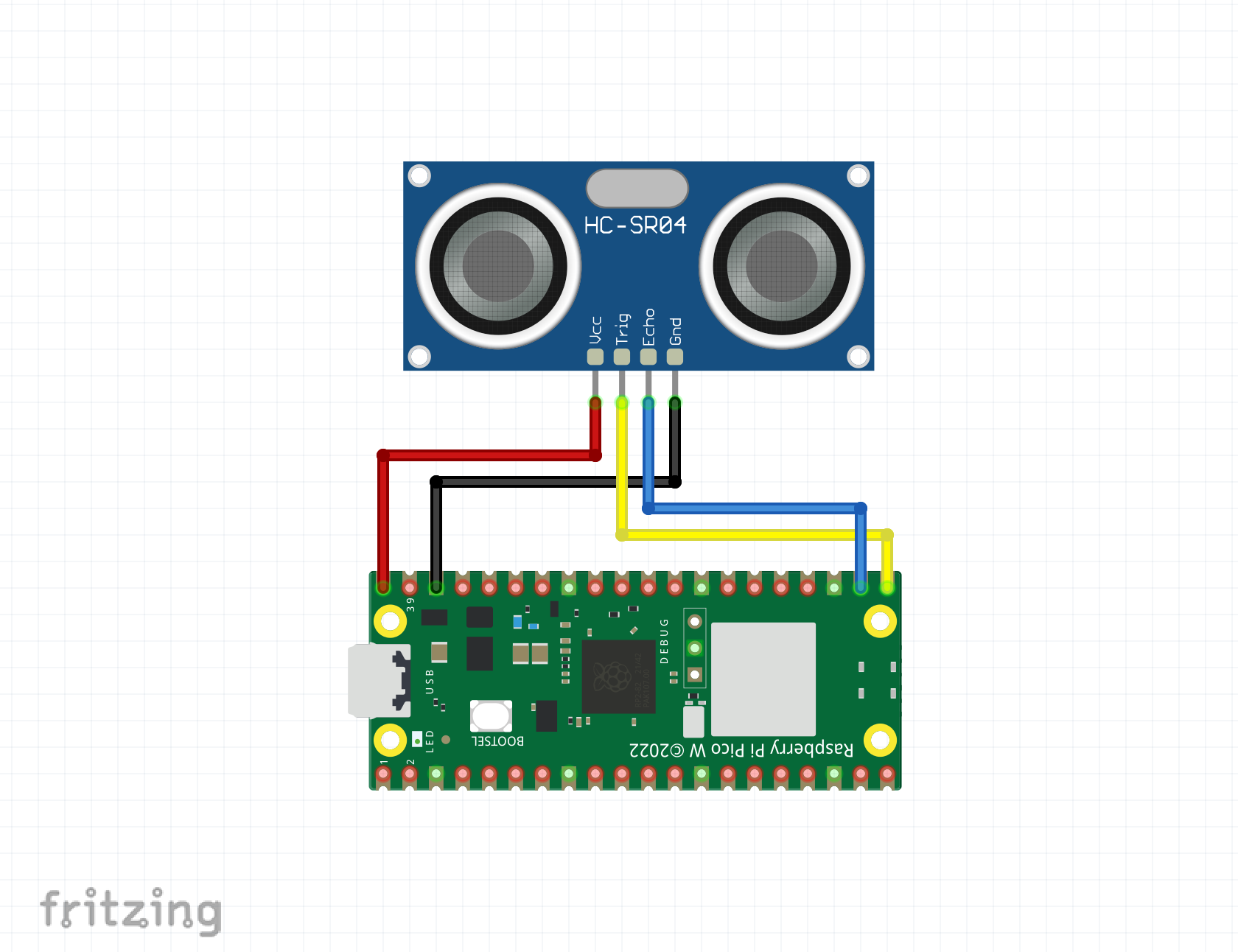
Wiring diagram
Formulas
There are two formulas used in the script:
- Timeout is calculated as th maximal possible distance (4m) multiplied by 2, as the acoustic burst must travel twice and then
multiplied by time of sound traveling 1m in us. The formula looks like this:
spec_max_distance * 2 * (sec_to_ms / speed_of_sound). - Distance is calculated as the measured delay converted to seconds, divided by 2, as back and forth travel and multiplied by speed of
sound converted to cm. Hence like this:
(delay / us_to_sec) / 2 * (speed_of_sound_in_cm).
MicroPython implementation
This implementation triggers every second, and the measured distance is in centimeters.
from machine import Pin, time_pulse_us
import time
# spec_max_distance * 2 * (sec_to_ms / speed_of_sound)
TIMEOUT = 24_000
def measure():
trigger = Pin(16, Pin.OUT)
echo = Pin(17, Pin.IN)
trigger.off()
echo.off()
time.sleep_us(5)
trigger.on()
time.sleep_us(10)
trigger.off()
delay = time_pulse_us(echo, 1, TIMEOUT)
# (delay / us_to_sec) / 2 * (speed_of_sound_in_cm)
return (delay / 1_000_000) / 2 * (344 * 100)
if __name__ == "__main__":
while True:
distance = measure()
print("Distance: {}".format(distance))
time.sleep(1)
If you would like to have a more robust solution, have a look at: https://github.com/rsc1975/micropython-hcsr04/blob/master/hcsr04.py
